
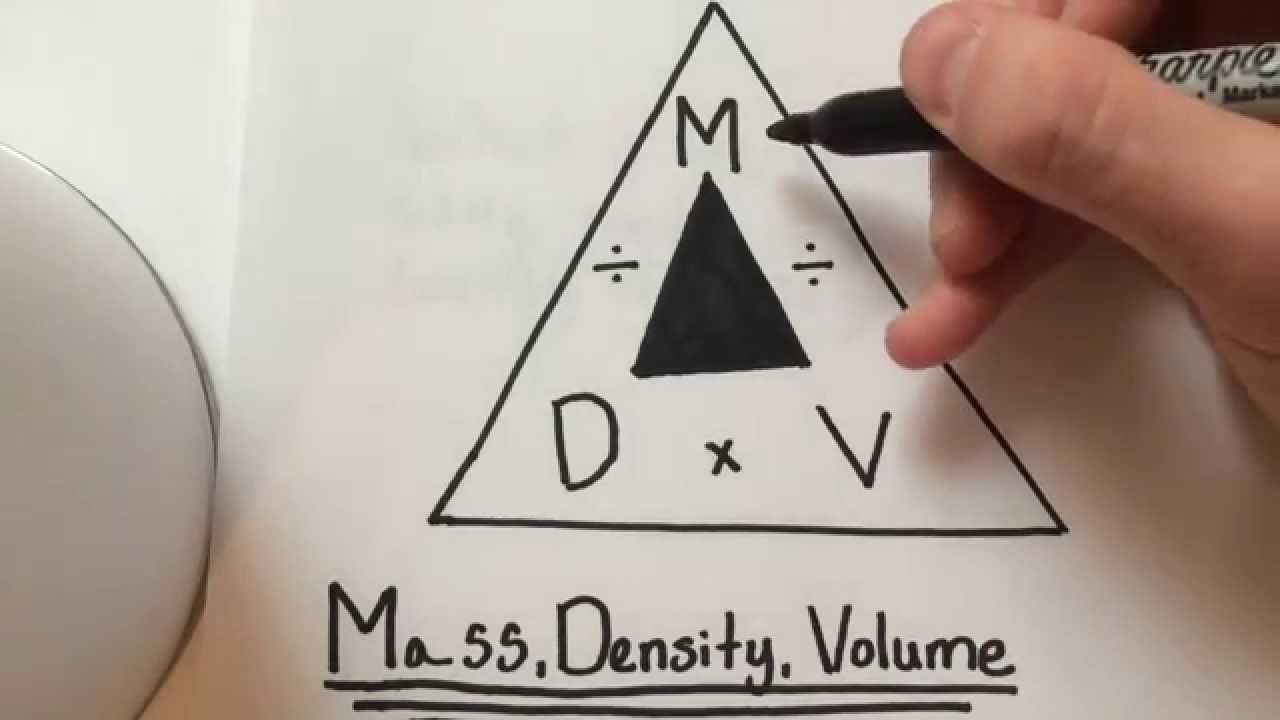
See also Thermophysical Properties of Air - density, viscosity, critical temperature and pressure, triple point, enthalpi and entropi, thermal conductivity and diffusicity. Molecular weights can be used to calculate Specific Gravity if the densities of the gas and the air are evaluated at the same pressure and temperature.

Ρ air = density of air (normally at NTP - 1.204 ) The Specific Gravity can be calculated as Specific Gravity of gases is normally calculated with reference to air - and defined as the ratio of the density of the gas to the density of the air - at a specified temperature and pressure. Example 4: Specific Gravity of Iron Specific Gravity for some common Materials Substance See also Thermophysical Properties of Water - Density, Freezing temperature, Boiling temperature, Latent heat of melting, Latent heat of evaporation, Critical temperature. Water is normally also used as reference when calculating the specific gravity for solids. SG of a fluid has the same numerical value as its density expressed in g/mL or Mg/m 3. Since Specific Gravity - SG - is dimensionless, it has the same value in the SI system and the imperial English system (BG).
It is common to use the density of water at 4 oC (39 oF) as a reference since water at this point has its highest density of 1000 kg/m 3or 1.940 slugs/ft 3. Ρ H2O = density of water - normally at temperature 4 oC Ρ substance = density of the fluid or substance Specific Gravity (Relative Density) - SG - is a dimensionless unit defined as the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water - at a specified temperature and can be expressed as
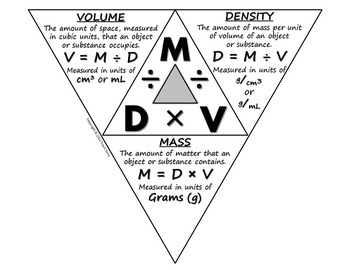
#FORMULA OF DENSITY HOW TO#
How to measure density of liquid petroleum productsĮxample 2: Using Density to Identify a MaterialĮxample 3: Density to Calculate Volume Mass Water - Density, Specific Weight and Thermal Expantion Coefficient - variation with temperature at 1, 68 and 680 atm, SI and Imperial unitsĪir - Density, Specific Weight and Thermal Expantion Coefficient - variation with temperature and pressure, SI and Imperial units Se also: Densities for some common materials Density is a physical property - constant at a given temperature and pressure - and may be helpful for identification of substances.īelow on this page: Specific gravity (relative density), Specific gravity for gases, Specific weight, Calculation examples On atomic level - particles are packed tighter inside a substance with higher density. See also Unit converter - mass and Unit converter - density
Slugs can be multiplied with 32.2 for a rough value in pound-mass (lb m). Note that there is a difference between pound-force (lb f) and pound-mass (lb m). The Imperial (U.S.) units for density are slugs/ft 3 but pound-mass per cubic foot - lb m/ft 3 - is often used.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
